Pacific Salmon
All kinds of Pacific salmon inhabit the Kamchatka coastal water. Salmon hatch in fresh water, migrate to the ocean, then return to fresh water to reproduce. Salmon find the way back to the spot they have hatched as they have an inner mechanism of native river sense. Salmon are believed to return to the exact spot they hatched to spawn. After entering the river, salmon cease feeding and develop a breeding dress. They undergo some body changes such as color change, humps, teeth and jaws growth as well as irreversible inner body changes.
All species participating in the migration and breeding are dying after spawning and giving life to a new generation. Salmon are the main and favorite food for many birds, animals, and especially for numerous Kamchatka bears.

King Salmon – Chavycha
(Oncorhynchus tshawytscha)

King salmon are the biggest and most valuable species of the Pacific salmon.
The scientific species name is based on the Russian common name chavycha, while Americans name them Chinook, which refers to the Chinook peoples, or king salmon.
Adult fish may be up to 1,5 m in length and gain 50 kg in weight. Chavycha are pacific salmon that thrive in the cold water. Early in June, at the age of 3-7 the adult fish return to their home rivers to spawn.
As a matter of fact, chavycha are considered to be king salmon due to their taste and dietary nutritional content. Each big species can give up to several kilograms of caviar. Chavycha salmon have large eggs with more than 5 mm in diameter.
Silver Salmon – Kizhuch
(Oncorhynchus kisutch)

The scientific species name is based on the Russian common name kizhuch.
Some adult fish may be up to 90 cm in length and gain up to 14 kg in weight. During their ocean phase, which is two years or more, silver salmon have silver sides and dark-blue backs. After entering fresh water, they develop dark-pink breeding dress. During their spawning phase, usually late August – September, their fins become black, their jaws and teeth become hooked. Kizhuch have the lowest fat content if compared to other salmon species. They are also the most warmth-loving ones.
Steelhead Salmon – Semga
(Oncorhynchus mykiss irideus)

Steelhead salmon live in the sea during the first four years then go to spawn in the rivers in September-November. During spawning, male steelhead salmon have a red stripe on the both sides. The juvenile steelhead live in the rivers for 1-4 years, then migrate to the sea.
Rainbow Trout – Mykizha
(Oncorhynchus mykiss)

Rainbow trout, including steelhead forms, usually inhabit and spawn in shallow, well-oxygenated rivers with gravel bottoms. Some species might be 80 cm in length and 3 kg in weight. The eggs are quite large up to 4-6 mm in diameter. During the summer, fall and winter seasons, mykizha usually inhabit the rivers without long migrations. In May, mykizha go to the rivers to spawn.
Body coloration is typically gold-green with white-grey belly covered with small dots. There is a bright reddish stripe going from gills to the tail. The recorded lifespan for a rainbow trout is 10 years.
Chum Salmon – Keta
(Oncorhynchus keta)

Chum Salmon are not fat fish with around 7% of fat. The biggest species reach 80 cm in length and 5 kg in weight. According to the time of spawning, there are 4 types of chum salmon. Monaco are small fish that go to spawn in May. Spring keta start to spawn from late May to early June. Summer keta usually spawn from July till early August. Fall keta spawn from late August till mid September. Keta come to the rivers from the sea with silver glance coloration. While migrating to spawning spots, they develop a wedding dress: their bodies become grey-yellow with lilac and dark pink streaks. During spawning, the coloration is almost black. Spawning males have enlarged teeth. Keta eggs are large in size and have bright-orange color.
Pink Salmon – Gorbusha
(Oncorhynchus gorbuscha)

The commercial harvest of pink salmon is a mainstay of fisheries in Kamchatka. The species size is up to 50 cm and weight is up to 4 kg. In the ocean, pink salmon are bright silver fish with dark spotting on the tail. After returning to their spawning streams, their colorings change. The dark spots appear on the head and sides. During their spawning migration, males develop pronounced humped backs, their jaws get longer and bent.
The fish return to the freshwater in July- August as two-year-old adults.
Red Salmon – Nerka
(Oncorhynchus nerka)

The name Red Salmon comes from the fact that these species are primarily red in hue, while caught in the sea. They can grow up to 80 cm in length and weigh 2-5 kg. Nerka’s habitat is cool water with temperature not more than +2. Spawning takes place in many rivers and lakes in Kamchatka. When they return to spawning grounds, they develop a wedding dress: their bodies become red, their heads turn green, and their fins become bloody red. They reach their sexual maturity at the age of 5-7.
There are three types of nerka: spring nerka spawning in July and early August, summer-fall nerka, and kokanee nerka dwelling in Kronotsky lake. They are smaller in size – 30 cm and weight 350 gr. The nerka fillet is amazing in taste. Caviar is quite small and has bright red coloring.
Arctik Char – Golets
(Salvelinus alpinus)

Arctik char are cold-water fish. In Siberia, they are known as golets. Char do not die after spawning like Pacific salmon and often spawn several times throughout their lives, typically every second or third year. The populations can be lacustrine, riverine or anadromous. Char are big in sizes, up to 88 cm in length and 15-16 kg in weight. They have silver bodies with big light spots and dark-blue backs. During spawning, males become dark, their backs turn green-brown, sides become brown-silver with numerous red and orange spots. Golets sometimes threaten smaller fish, such as small-mouth char and long finned char.
Kundzha
(Salvelinus leucomaenis)

Kundzha are a species of fish in the Char family. They are endemic only to the Far East of Kamchatka. They are also known as Siberian White Spotted Char. They have green coloring with lilac hue. During spawning, coloring intensifies and kundzha look darker. They migrate up the rivers to spawn.
Kundzha are ferocious fish. They have a very toothy mouth with sharp teeth. They live on the salmon smolt and young Dollies that are so plentiful in the rivers of Kamchatka. They can reach 90 cm in length and 6 kg in weight.
Grayling – Kharius
(Oncorhynchus nerka)

Grayling are species of freshwater fish in the Salmon family. They are endemic to Kamchatka. Grayling grow up to 50 cm in length and 1,5 kg in weight. The lifespan is approximately 10 years.
Grayling color is typically plain and become darker with age. Females are usually lighter than males. The back of the head and the body are dark brown with violet hue. The low jaw is white or light grey; the jaw front edge is black. There are two big symmetric black spots on the low jaw. The belly is black or light grey from pectoral fins to anal ones. The tail has copper red coloring.
Grayling occur primarily in cold waters of mid-sized to large rivers and lakes, returning to rocky streams to breed. Numerous populations of grayling inhabit river, such as Penzhina, Kamchatka, and Talovka. There is not a lot of commercial fishing of grayling, but amateur or sport fishing is very popular.
Grayling are typical predators. They feed on small prey items, such as juvenile fish of pink and dog salmon. Bigger grayling might feed on shrewmouse or field mouse fallen into the water. Kamchatka grayling can be easily caught on small bloons (less than 35-40 mm) or medium bloons (40-50 mm) as well as on fluctuation spoon-baits 50-65 mm in length for effectiveness: throwing-catching (the quality of production is crucial for these types).
It is important to keep in mind, as long as there are fish of high rank in the water, grayling catching doesn’t occur. The fish rank is the following: mikizha #1,white golets and kundzha # 2, malma # 3, and finally grayling.
SEA FISH
Pacific Cod

Cod is the common name for the demersal fish genus Gadus, belonging to the family Gadidae
The Pacific cod (Gadus macrocephalus), found in both eastern and western regions of the northern Pacific. Cod is popular as a food with a mild flavour and a dense, flaky, white flesh. Cod livers are processed to make cod liver oil, an important source of vitamin A, vitamin D, vitamin E, and omega-3 fatty acids (EPA and DHA).
Pacific Cod:
Scientific name – Gadus macrocephalus
Maximum length – 119 cm
Maximum weight – 22.7 kg
Maximum age – 18 year
Saffron Cod

The saffron cod is a commercially harvested fish closely related to true cods. It is dark grey-green to brown, with spots on its sides and pale towards the belly. It may grow to 60 cm and weigh up to 1.3 kg.
Family: Gadidae
Scientific name: Eleginus gracilis
Higher classification: Eleginus
Halibuts
Pacific Halibut

Pacific halibut, is a species of righteye flounder. This very large species of flatfish is native to the North Pacific and is fished by commercial fisheries, sport fishers, and subsistence fishers.
Scientific name – Hippoglossus stenolepis)
Maximum length 470 cm
Maximum weight 360 kg
Usually 40-90 cm length and 6-9 kg weight
They are among the largest teleost fishes in the world. From November to March, mature halibut concentrate annually on spawning grounds along the edge of the continental shelf at depths from 183 to 457 m (600 to 1,499 ft).
Arrow toothhedHalibut (Atheresthes)

Arrow ToothheadHalibut (Atheresthes) is a genus of righteye flounders native to the north Pacific Ocean
Maximum length 100 cm, Usually 45-70 cm
Maximum weight 8,5 kg. Usually 15,-3,0 kg
Maximum age 33 years
Mature halibut concentrate annually at depths from 25 to 1200 m (82 to 3,900 ft).
Greenland Halibut

The Greenland halibut or Greenland turbot (Reinhardtius hippoglossoides) belongs to the Pleuronectidae family (the right eye flounders), and is the only species of the genus Reinhardtius. It is a deep water fish, ranging between about 200 and 1,600 m (700 and 5,200 ft), and is found in the northern Pacific Oceans
Maximum length 1,2 m
Maximum weight 45 kg
Flounders
Flounders are a group of flatfish species. They are demersal fish, found at the bottom of oceans around the world.
The name “flounder” is used for several only distantly related species, though all are in the suborder Pleuronectoidei (families Achiropsettidae, Bothidae, Pleuronectidae, Paralichthyidae, and Samaridae).
Lepidopsetta
is a genus of righteye flounders native to the North Pacific Ocean.
Klass : Actinopterygii
Rock Sole
The rock sole (Lepidopsetta bilineata) is a flatfish of the family Pleuronectidae. It is a demersal fish that lives on sand and gravel bottoms at depths of up to 575 metres (1,886 ft), though it is most commonly found between 0 and 183 metres (0 and 600 ft). Its native habitat is the temperate waters of the northern Pacific, from Baja California to Alaska, the Aleutian Islands and southeastern parts of the Bering Sea. It grows up to 60 centimetres (24 in) in length and can weigh up to 1.8 kilograms (4.0 lb), and has a maximum recorded lifespan of 22 years.
Northern Rock Sole
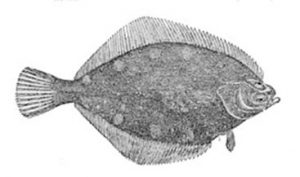
The northern rock sole (Lepidopsetta polyxystra) is a flatfish of the family Pleuronectidae. It is a demersal fish that lives on sand, mud and gravel bottoms at depths of up to 700 metres (2,300 ft), though it is most commonly found between 19 and 246 metres (62 and 807 ft). Its native habitat is the temperate waters of the northern Pacific, from Puget Sound to Alaska (overlapping the range of the rock sole), the Aleutian Islands and across the Bering Sea to the Kuril Islands and the Sea of Okhotsk (overlapping the range of the dusky sole). Males grow up to 69 centimetres (27 in) in length, whilst females can reach 49 centimetres (19 in). The maximum recorded lifespan is 18 years.
Yellowfin Sole

The yellowfin sole (Limanda aspera) is a flatfish of the family Pleuronectidae. It is a demersal fish that lives on soft, sandy bottoms at depths of up to 700 metres (2,300 ft), though it is most commonly found at depths of around 91 metres (299 ft). Its native habitat is the temperate waters of the northern Pacific, from Korea and the Sea of Japan to the Sea of Okhotsk, the Bering Sea and Barkley Sound on the west coast of Canada. Males grow up to 49 cm (19 in) in length, though the common length is around 33.5 cm (13.2 in). The maximum recorded weight is 1.7 kg (3.7 lb), and the maximum recorded lifespan is 26 years
The yellowfin sole has a deep body, with a small mouth, moderately large and closely situated eyes, and a slightly pronounced snout. The upper side of the body is olive to brown in colour, with dark mottling, and dorsal and anal fins are yellowish on both sides of the body, with faint dark bars and a narrow dark line at the base. Scales are rough on both sides of the body
Starry Flounder

The Starry Flounder (Platichthys stellatus), also known as the grindstone, emerywheel and long-nosed flounder, is a common flatfish found around the margins of the North Pacific.[2] The distinctive features of the starry flounder include the combination of black and white-to-orange bar on the dorsal and anal fins, as well as the skin covered with scales modified into tiny star-shaped plates or tubercles (thus both the common name and species epithet), resulting in a rough feel. The eyed side is black to dark brown, while the lower side is white or cream-colored. Although classed as “righteye flounders,” individuals may have their eyes on either the right or left side. They have been recorded at up to 91 cm and 9 kg.
Dusky Sole

(Lepidopsetta mochigarei) is a flatfish of the family Pleuronectidae. It is a demersal fish that lives on bottoms in the temperate waters of the northwest Pacific, from the Korean peninsula to the southern Sea of Okhotsk. It grows up to 40 centimetres (16 in) in length.
Yellow-bellied flounder

Pleuronectes quadrituberculatus – Platessa guadrituberculata – Flounder
Maximum length 50-60 cm
Maximum weight 3 kg
ATKA MACKEREL

Atka Mackerel ( Pleurogrammus Monopterygius) The Atka mackerel (Pleurogrammus monopterygius) is a mackerel in the family Hexagrammidae. Atka mackerel are common to the northern Pacific ocean
Adults have five vertical, blackish bands on their bodies,[7] which are normally yellowish.
Atka mackerel can generally be found from the intertidal zone to depths up to 575 meters
ALASKA POLLACK

Alaska pollock is a member of the cod family, reflected by some of its other names
Alaska pollock weigh 1/2 to 2 pounds and average 12 to 20 inches in length. Fillets average 2 to 3 ounces. Larger fillets of 4 to 6 ounces are available in the fall.
RED ROCKFISH

Market Name(s): Snapper, Pacific snapper, rockfish, rock cod, black bass (assorted species names: bocaccio, chilipepper, Pacific ocean perch, etc.)
There are almost 70 species of rockfish found in the Eastern Pacific,
The yelloweye rockfish is colored red on its back, orange to yellow on the sides, and black on the fin tips. Its young are typically under 28 cm (11 in) in length, and differ from the adults in that they have two reddish-white stripes along their belly,[3] and are often red
They grow to a maximum length of 36 in (0.9 m) and are typically found in the 28-to-215-fathom (51-to-393 m) range, although specimen have been reported up to a maximum depth of 260 fathoms (475 m
